- المعلم: salah hadji
University of Souk Ahras
نتائج البحث: 217
- المعلم: Sassi AOUADI
- المعلم: Abdelouahab MESSOUBER
Short Summary of Special Relativity
Special Relativity is based on two principles:
-
The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames.
-
The speed of light (c) is constant for all observers.
From these follow the key effects:
-
Time dilation: moving clocks tick more slowly.
-
Length contraction: moving objects shrink along the direction of motion.
-
Relativity of simultaneity: simultaneity depends on the observer.
Space and time form a unified space-time.
Events are separated by an invariant interval:
[
ds^2 = c^2 dt^2 - dx^2 - dy^2 - dz^2.
]
Motion in space-time is represented by worldlines.
The light cone divides space-time into past, future, and elsewhere.
Relativistic dynamics is governed by four-vectors, such as:
-
position (x^\mu),
-
four-momentum (p^\mu = (E/c, \vec{p})),
-
four-current (j^\mu),
-
electromagnetic four-potential (A^\mu).
Energy and momentum satisfy:
[
E^2 = p^2 c^2 + m^2 c^4.
]
Proper time (d\tau) is the time measured by the moving particle:
[
d\tau = \frac{dt}{\gamma}.
]
- المعلم: Kamel ALIOUA
- المعلم: Abdelouahab MESSOUBER
Les plantes occupent une place fondamentale dans notre monde et en particulier dans les écosystèmes terrestres. Elles assurent la production primaire, construisent des couverts végétaux, élaborent et structurent les sols. Elles participent aussi fortement à la régulation du climat et au cycle de l’eau. En matière de contributions à la nature, leur rôle est donc primordial. Nous n’imaginons pas un paysage sans les plantes, au point d’appeler désert ou minéral un environnement dans lequel le couvert végétal est réduit ou presque absent.
La biodiversité des plantes est un patrimoine clef pour la recherche végétale. Les sélectionneurs ne peuvent pas prendre le risque de la mettre en péril. Ils ont donc toujours préservé les ressources génétiques, base de leur travail d’amélioration des plantes. Qu’il s’agisse d’anciennes populations ou de variétés plus récentes.
La diversité biologique des plantes est gigantesque : environ quatre cent mille espèces de plantes terrestres sont ainsi déjà connues pour la science, et chaque année apporte son tribut de nombreuses espèces nouvelles découvertes par les chercheurs. Mais cette diversité de plantes n’est pas également répartie à la surface du globe.
- المعلم: Nadia CHIAHI
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI
- المعلم: Salima Meziane
- المعلم: abderrahim boutemedjet
- المعلم: Fahima Djefaflia
- المعلم: abderrahim boutemedjet
- المعلم: Fahima Djefaflia
- المعلم: abderrahim boutemedjet
- المعلم: Fahima Djefaflia
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF

- المعلم: Issam BEN DAHMENE
- المعلم: Naima HABIB
- المعلم: Nadjette KIAS
- المعلم: Abd-Ennour SAMMAR
- المعلم: louardi YANDJAH
The objectives of Data Structures and Algorithms module can be summarized in these points as follow:
- Manipulate hash tables and know the different operations that can be manipulated on this type of data and more precisely demonstrate several approaches: linear and quadratic probing, double hashing, and separate chaining to resolve the collision problem while using OOP and more particularly the use of JAVA language.
- Covering the simplest popular tree structure: binary trees in the general case and binary search trees more specifically, know the different operations that can be manipulated on these types of data and more precisely know the different paths to follow to visit the nodes of a binary tree in using different recursive methods and demonstrating insertion, deletion, and search, min and maxf. And finally, implementing binary search trees in Java.
- Study balanced trees (AVL) and know the different types of rotation to apply during additions or insertions so that the AVL tree can preserve its type. Implement AVLs in Java.
- Explaining red-black trees, one of the most efficient balanced trees. Then demonstrates the rotations and color switches necessary to balance the tree
- Explore the notion of graphs, some concepts, types of graphs, how to represent graphs, implement graphs, calculation of the shortest path (disjkistra algorithm)
This module is aimed at master 1 students specializing in web and artificial intelligence
- المعلم: Samia DRICI
Intitulé du Master : Physique des Rayonnements
Semestre : 2
Intitulé de l’UE : Découverte
Intitulé de la matière : Introduction to Astrophysics
Crédits : 2
Coefficients : 2
Teaching objectives:
The course "Introduction to Astrophysics" offered in the Master's program in Radiation Physics for the second semester focuses on a comprehensive introduction to astrophysics, an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of physics and astronomy. This fascinating area aims to understand the underlying mechanisms governing celestial objects such as stars, planets, galaxies, and the interstellar medium, based on fundamental physical principles.
The objectives of this 2-credit course, with a coefficient of 2, include:
- Introduction to fundamental concepts: Students will be introduced to key astrophysics concepts, including the properties of celestial objects (like their luminosity, mass, temperature, and movement in space).
- Interdisciplinary understanding: This course aims to bridge pure physics and astronomy, allowing students to understand how physical principles apply to the universe.
- Initiation to astrophysics research: Students will be encouraged to develop an interest in astrophysics research by exploring the latest discoveries and theories in the field.
The assessment method is divided equally into two parts: 50% based on continuous assessment, which may include homework, presentations, or projects during the semester, and 50% on a final exam. This assessment method is designed to ensure that students not only master the theory but also actively engage in learning throughout the semester.
This course is designed to be a gateway to the extraordinary universe of astrophysics, providing students with the tools and knowledge necessary to pursue further studies or a career in this exciting field.

The field of chemistry has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years due to the ever-increasing power and accessibility of computers. This has led to the development of a vast array of sophisticated computer tools that are now essential for many aspects of chemical research and development.
This introductory course will provide students with a basic understanding of the most important computer tools used in chemistry. We will cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Molecular modeling: This involves using computers to build and manipulate models of molecules. This can be used to study the structure and properties of molecules, as well as to design new molecules with specific properties.
- Computational chemistry: This is the use of computers to solve the equations of quantum mechanics in order to study the behavior of atoms and molecules. This can be used to predict the properties of molecules, as well as to understand the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
- Chemicalinformatics: This is the use of computers to manage and analyze chemical data. This can be used to search for new drugs, to design new materials, and to understand the environmental impact of chemicals.
- Spectroscopy: This is the study of the interaction of matter with electromagnetic radiation. Computers are used to acquire and analyze spectroscopic data, which can be used to identify and characterize molecules.
- المعلم: Rafik BENSEGUENI

Lab: Extraction and Physicochemical Analysis Methods
This practical course helps students learn the essential knowledge and skills needed to select and use the best methods for testing the quality and analyzing pharmaceutical products, like raw materials, related substances, and finished drugs, according to official standards.
Learning Objectives
- Understand and apply the main extraction techniques used to isolate active compounds from natural or synthetic sources.
- Perform physicochemical analyses for qualitative and quantitative determination of pharmaceutical substances.
- Develop analytical reasoning to select the suitable method according to the chemical nature of the compound.
Recommended Prerequisites
Basic knowledge of organic chemistry and physicochemical analytical techniques.
- المعلم: Soumaya BATOUCHE
- المعلم: Mohamed ZABAT
This course is dedicated to the students of the 2nd year of electronic Bachelor degree
- المعلم: Mohammed Saaidia

- المعلم: Billel Ali srihen
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE

- المعلم: Billel Ali srihen
This module is about grammar' rules and the translation of important legal terms and texts from Arabic to English and vice versa. It aims at helping students to use English for Law. Thus in this handout, I have provided them with some basic lessons and their translation as well as the legal terms in relevance.
- المعلم: Siham GOUASMIA
- المعلم: Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
This module explores the fundamental principles and phenomena related to the surfaces and interfaces of materials, that is, at the boundary separating two bulk phases.
A hyphen or a slash between the two bulk phases involved, such as solid-liquid or solid/liquid, is used to signify the interface. Because gases are entirely miscible, there is no interface between them. Dissolution, crystallisation, corrosion, heterogeneous catalysis, electrode processes, and other important phenomena occur at the interface.
It covers topics such as adsorption, desorption, surface tension, and the properties of colloids and surfactants. Students will learn about the significance of surface phenomena in various scientific and industrial applications, including catalysis, material science, and environmental science. The module aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how surfaces influence the behavior of materials and how surface modifications can be used to enhance their properties.
- المعلم: Wahiba Bessashia
- المعلم: Nadia BENATI

'objectif de la matière
Apporter les connaissances spécifiques pour aborder un travail de recherche de haut niveau sur les nouveaux matériaux. Former aux fonctions de cadre et/ou d’expert relevant de la recherche et développement dans le domaine des matériaux.
- المعلم: Siham KERMICHE
As part of helping our students deepen this knowledge, I offer this modest educational support, entitled: modeling and simulation of electrical machines, which is aimed at Master1 students in Electromechanics.
The overall objective of this support is to establish the mathematical models necessary for the modeling and simulation of electrical machines. This modeling is based on the calculation of the magnetic interactions between the different windings constituting the machine studied. These models provide, for the machine considered, the instantaneous and steady-state equations, the performances and the control laws.
The student must have the following knowledge:
- Three-phase electrical circuits, magnetic circuits, single-phase and three-phase transformers.
- Direct and alternating current electrical machines.
Pr. Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
Subject: Modeling and simulation of Electrical Machines
Domain: Science and technology
Sector: Electromechanics
****************************************************************************************
Dans le cadre d’aider nos étudiants à approfondir ces connaissances, je propose ce modeste support pédagogique, intitulé: modélisation et simulation des machines électriques, qui s’adresse aux étudiants du Master1 en Electromécanique.
L’objectif global de ce support est établie les modèles mathématiques nécessaires pour la modélisation et la simulation des machines électriques. Cette modélisation est basée sur le calcul des interactions magnétiques entre les différents enroulements constitutifs de la machine étudiée. Ces modèles fournissent, pour la machine considérée, les équations instantanées et en régime établi, les performances et les lois de commande.
L’étudiant devra posséder les connaissances suivantes :
- Circuits électriques triphasés, circuits magnétiques, transformateurs monophasés et triphasés.
- Machines électriques à courant continu et alternatif.
Pr. Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
Matière : Modélisation et simulation des Machines Electriques
Domaine : Sciences et technologie
Filière : Electromécanique
- المعلم: Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
Lecturer: Prof. Manel BOULOUDENINE
This module introduces the fundamental principles of classical mechanics through the study of the motion of a material point. It covers the basic concepts of kinematics and dynamics, including reference frames, velocity, acceleration, forces, Newton’s laws of motion, work and energy, and conservation principles. Emphasis is placed on developing physical intuition and problem-solving skills essential for understanding more advanced topics in physics and engineering.
- المعلم: Manel BOULOUDENINE

-Matière : Qualité de l’énergie électrique.
Public cible : master 1 machine électrique.
· Les objectifs généraux :
- Etudier les phénomènes principaux qui détériorent la Qualité de l'Energie Electrique (QEE), leurs origines et les conséquences sur les équipements à travers la dégradation de la tension et/ou du courant et les perturbations sur les réseaux.
- Comprendre l'implication des charges non linéaires dans la détérioration de la qualité de l'énergie et prendre connaissance des principales solutions pour l'améliorer en remédiant aux perturbations en les éliminant ou en les atténuants lorsqu’elles sont inévitables.
- المعلم: hesna aberkane
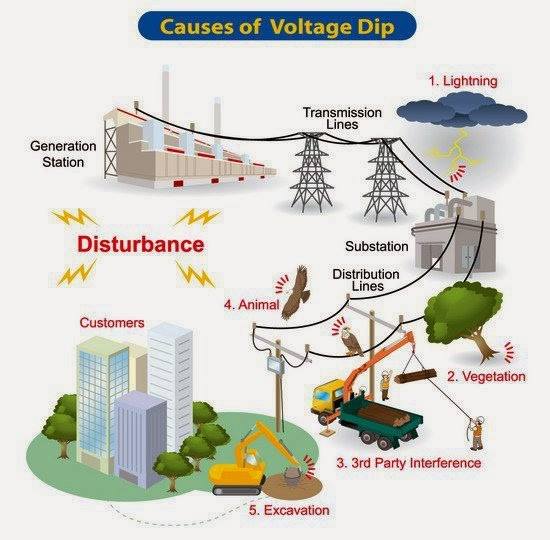
The electric grid network is the backbone of modern electrical power systems, facilitating the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity to consumers. It comprises interconnected power plants, transmission lines, substations, and distribution networks that work together to deliver electricity reliably and efficiently. The grid operates at various voltage levels, from high-voltage transmission lines that transport electricity over long distances to lower-voltage distribution lines that deliver power to homes and businesses. Grid operators continuously monitor and manage the flow of electricity to balance supply and demand, ensuring stable and reliable power delivery. With the integration of renewable energy sources and advancements in grid technologies, such as smart grids and energy storage systems, the electric grid network is evolving to meet the challenges of sustainability, resilience, and energy security in the 21st century. Understanding the complexities of the electric grid network is essential for optimizing its operation, improving its resilience, and transitioning towards a more sustainable energy future.
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
The module is divided into six chapters:
- Chapter 1: The student must know the fundamental concepts of the structure of matter, a presentation of the different types of transformations, concentrations and solutions.
- Chapter 2: It is devoted to the study of the main constituents of matter: Demonstrations through certain experiments, such as those of JJ Thomson and Rutherford…
- Chapter 3: It is devoted to radioactivity and types of nuclear reactions.
- Chapter 4: The study of the electronic structure of the atom is addressed in this chapter, from the notion of the probability of presence to the different rules of construction of the electronic structure of the atom and the periodic classification of the elements.
- Chapter 5: It concerns D. Mendeleev's periodic classification and the evolution and periodicity of the physico-chemical properties of the elements.
- Chapter 6: It is devoted to the study of the different types of bonds, the geometry of molecules with the VSEPR theory and chemical bonding in the quantum model by introducing the concept of hybridization and giving its link with the VSEPR theory.
- المعلم: Tahar ABBAZ
- المعلم: Youcef HAMLAOUI

This laboratory manual accompanies the first–year physics course in Science and Technology. It provides students with structured experimental activities that develop both conceptual understanding and scientific skills. Through experiments such as Measurements and Error Analysis, Free Fall, Simple Pendulum, Uniformly Accelerated Rectilinear Motion (Newton’s Law), and Torsion Pendulum and Moment of Inertia, students learn to connect theory with observation, analyse data critically, and apply the scientific method with rigor and autonomy. The manual encourages precision, reasoning, and curiosity — essential qualities for future scientists and engineers.
- المعلم: SEDRATI Rafik
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI
- المعلم: Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA

Le cours de Véhicules Électriques explore l'importance croissante des véhicules électriques (VE) dans la réduction du bruit, de la pollution et de la dépendance au pétrole, notamment lorsque l'énergie utilisée provient de sources renouvelables. Le module se concentre sur les principes fondamentaux de la conception des VE, en abordant les enjeux technologiques et environnementaux associés.
Les premiers chapitres retracent l'évolution historique des VE, les contributions des inventeurs et ingénieurs clés, et identifient les principaux constructeurs mondiaux de voitures électriques. Le cours permet également de classifier les différents types de VE.
Dans les chapitres suivants, les étudiants étudieront en détail les différentes technologies de batteries, les machines électriques et les équipements auxiliaires, ainsi que les structures et les aspects de protection des véhicules. Ces éléments sont essentiels pour comprendre le fonctionnement et la conception des véhicules électriques modernes.
- المعلم: salaheddine farhi
- المعلم: souheila bouacherine
- المعلم: Leila Mahfoudi

Programme
Chap.1: Types cellulaires
Chap.2: La structure membranaire
Chap.3: Transports et diffusions a travers la membrane plasmique des petites et des macromolécules
Chap.4: Le cytosquelette et ses fonctions biologiques
Chap.5: Le systéme endo-membranaire
Chap.6: Le noyau et la division cellulaire
- المعلم: Amine BERGHICHE

- المعلم: Issam BEN DAHMENE
- المعلم: Nor REBAH
- المعلم: Nor REBAH
- المعلم: louardi YANDJAH
Dimensional analysis is a method used to verify the consistency of physical equations by ensuring that all quantities involved share the same fundamental dimensions (length [L], mass [M], time [T], etc.). It helps to understand the relationships between variables in a phenomenon and to build simplified physical models using dimensionless quantities. Vectors, on the other hand, are mathematical entities defined by a direction, a sense, and a magnitude. They represent physical quantities such as force, velocity, and acceleration. Vector operations addition, dot product, and cross product are used to describe interactions and motion in space. Together, these concepts form the foundation of rigorous physical reasoning applied throughout all fields of engineering.
- المعلم: Kamel ALIOUA
- المعلم: Fahima Djefaflia
- المعلم: louardi YANDJAH
يعد هذا المقرر مدخلا تأسيسيا لعلم اجتماع المنظمات، حيث يهدف إلى تزويد الطلبة بالمعارف الأولية والأساسية التي تمكنهم من فهم المنظمات كظواهر اجتماعية معقدة.
يتناول المقرر التعريف بعلم اجتماع المنظمات كحقل معرفي مستقل، ويقدم المفاهيم الرئيسية مثل المنظمة، البيروقراطية، الهيكل التنظيمي، السلطة، والثقافة التنظيمية. كما يستعرض أهم النظريات السوسيولوجية التي ساهمت في فهم وتحليل المنظمات، من النظريات الكلاسيكية إلى المقاربات الحديثة.
يركز المقرر على تطوير القدرات التحليلية للطلبة من خلال دراسة أنماط العلاقات الاجتماعية، أشكال التنظيم، آليات اتخاذ القرار، والتفاعلات الإنسانية داخل المنظمات المختلفة. كما يسعى إلى إكساب الطلبة منهجية علمية في دراسة الظواهر التنظيمية تمهيدا للتعمق في المستويات التعليمية اللاحقة.
من خلال هذا المقرر، سيتمكن الطالب من بناء قاعدة معرفية تؤهله لفهم ديناميكيات المنظمات في المجتمع المعاصر، وتمنحه الأدوات الأولية للتحليل السوسيولوجي للمؤسسات التي يتفاعل معها في حياته الأكاديمية والمهنية المستقبلية.
- المعلم: djouhaina guerdaoui
- المعلم: Atef BENHAOUES
- المعلم: Daoud SEKKI
- المعلم: Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
- المعلم: Naziha ZERARI
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI

- المعلم: Nouredine GASMALLAH
- المعلم: Nadjette KIAS
The “Reinforced Concrete Structures” module has as its main objective to enable Master 1 Materials students to select and apply appropriate calculation methods for the design and reinforcement of elements constituting a reinforced concrete structure.
During this module, you will be expected to:
-
Understand the properties of concrete and steel and their interaction within structures.
-
Apply calculation and design methods for various structural elements according to current standards.
-
Connect theory to practice through the analysis of real case studies.
By the end of this module, you will be able to design and reinforce reinforced concrete structures, taking into account the technical and structural constraints specific to construction projects.
- المعلم: Naoui GOUASMIA
- المعلم: Siham KERMICHE
- المعلم: salaheddine farhi
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI
- المعلم: Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
- المعلم: Naziha ZERARI
Département : sciences sociales
Module : langue étrangère (français) 1 année master sociologie de l’éducation
Prof : Bouamrane Abdallah année univ : 2023.2024
Texte support : Education et sociologie de Durkheim
« …….La doctrine de Durkheim de l’éducation est un élément essentiel de sa sociologie. « Sociologie, dit-il, c’est surtout en sociologie que je vous parlerai d’éducation. D’ailleurs, bien loin qu’à procéder ainsi on s’expose à voir et à montrer les choses par un biais qui les déforme, je suis, au contraire, convaincu qu’il n’est pas de méthode plus apte à mettre en évidence leur véritable nature. » L’éducation est chose éminemment sociale.
L’observation le prouve. D’abord, dans chaque société, il y a autant d’éducations spéciales qu’il y a de milieux sociaux différents. Et, même dans des sociétés égalitaires comme les nôtres, qui tendent à éliminer les différences injustes, l’éducation varie et doit nécessairement varier, selon les professions. Sans doute, toutes ces éducations spéciales reposent sur une base commune. Mais cette éducation commune varie d’une société à l’autre. Chaque société se fait un certain idéal de l’homme. C’est cet idéal « qui est le pôle de l’éducation ». Pour chaque société, l’éducation est « le moyen par lequel elle prépare dans le cœur des enfants les conditions essentielles de sa propre existence ». Ainsi, « chaque type de peuple a son éducation qui lui est propre et qui peut servir à le définir au même titre que son organisation morale, politique et religieuse ». L’observation des faits conduit donc à la définition suivante : « L’éducation est l’action exercée par les générations adultes sur celles qui ne sont pas encore mûres pour la vie sociale. Elle a pour objet de susciter et de développer chez l’enfant un certain nombre d’états physiques, intellectuels et moraux que réclament de lui et la société politique dans son ensemble et le milieu spécial auquel il est particulièrement destiné ». Plus brièvement, « l’éducation est une socialisation… de la jeune génération ».
Mais pourquoi en est-il nécessairement ainsi ? C’est « qu’en chacun de nous, peut-on dire, il existe deux êtres qui, pour être inséparables autrement que par abstraction, ne laissent pas d’être distincts. L’un est fait de tous les états mentaux qui ne se rapportent qu’à nous-mêmes et aux événements de notre vie personnelle : c’est ce qu’on pourrait appeler l’être individuel. L’autre est un système d’idées, de sentiments et d’habitudes, qui expriment en nous, non pas notre personnalité, mais le groupe ou les groupes différents dont nous faisons partie ; telles sont les croyances religieuses, les croyances et les pratiques morales, les traditions nationales ou professionnelles, les opinions collectives de toutes sortes. Leur ensemble forme l’être social. Constituer cet être en chacun de nous, telle est la fin de l’éducation. » Sans la civilisation, l’homme ne serait qu’un animal. C’est par la coopération et par la tradition sociales que l’homme s’est fait homme. Moralités, langages, religions, sciences sont des œuvres collectives, des choses sociales. Or, c’est par la moralité que l’homme forme en lui la volonté, qui dépasse le désir ; c’est le langage qui l’élève au-dessus de la pure sensation ; c’est dans les religions d’abord, puis dans les sciences, que s’élaborent les notions cardinales dont est faite l’intelligence proprement humaine. — « Cet être social n’est pas donné tout fait dans la constitution primitive de l’homme… C’est la société elle-même qui, à mesure qu’elle s’est formée et consolidée, a tiré de son propre sein ces grandes forces morales… L’enfant, en entrant dans la vie, y apporte que sa nature d’individu. La société se trouve donc, à chaque génération nouvelle, en présence d’une table presque rase sur laquelle il lui faut construire à nouveaux frais. Il faut que, par les voies les plus rapides, à l’être égoïste et asocial qui vient de naître, elle en surajoute un autre, capable de mener une vie morale et sociale. Voilà quelle est l’œuvre de l’éducation. » L’hérédité transmet les mécanismes instinctifs qui assurent la vie organique et, chez les animaux qui vivent en sociétés, une vie sociale assez simple. Mais elle ne suffit pas à transmettre les aptitudes que suppose la vie sociale de l’homme, aptitudes trop complexes pour pouvoir « se matérialiser sous la forme de prédispositions organiques ». La transmission des attributs spécifiques qui distinguent l’homme se fait par une voie qui est sociale, comme ils sont sociaux : c’est l’éducation.
Pour l’esprit exercé à regarder les choses de ce biais, cette conception sociologique de la nature et du rôle de l’éducation s’impose avec la force de l’évidence. Durkheim l’appelle : un axiome fondamental. Disons plus exactement : une vérité d’expérience. Nous voyons clairement, quand nous pensons en historien, que l’éducation à Sparte, c’est la civilisation lacédémonienne faisant des Spartiates pour la cité lacédémonienne ; — que l’éducation athénienne, au temps de Périclès, c’est la civilisation athénienne faisant des hommes conformes au type idéal de l’homme, tel que le conçoit Athènes à cette époque, pour la cité athénienne et, en même temps, pour l’humanité, telle qu’Athènes se la représente dans ses rapports avec elle. Il nous suffit d’anticiper sur l’avenir pour comprendre comment les historiens interpréteront l’éducation française au xxe siècle : même dans ses tentatives les plus audacieusement idéalistes et humanitaires, elle est un produit de la civilisation française ; elle consiste à la transmettre ; bref, elle cherche à faire des hommes, conformes au type idéal de l’homme qu’implique cette civilisation, à faire des hommes pour la France, et aussi pour l’humanité, telle que la France se la représente dans ses rapports avec elle.
Pourtant, cette vérité d’évidence a été généralement méconnue, surtout au cours des derniers siècles. Philosophes et pédagogues sont d’accord pour voir, dans l’éducation, une chose éminemment individuelle. « Pour Kant, écrit Durkheim, pour Kant comme pour Mill, pour Herbart comme pour Spencer, l’éducation aurait avant tout pour objet de réaliser, en chaque individu, mais en les portant à leur plus haut point de perfection possible, les attributs constitutifs de l’espèce humaine en général. » Mais cet accord n’est pas une présomption de vérité. Car nous savons que la philosophie classique a presque toujours oublié de considérer l’homme réel d’un temps et d’un pays, le seul qui soit observable, pour spéculer sur une nature humaine universelle, produit arbitraire d’une abstraction faite, sans méthode, sur un nombre très restreint d’échantillons humains. On admet généralement aujourd’hui que son caractère abstrait a faussé, dans une large mesure, la spéculation politique du xviiie siècle, par exemple : individualiste à l’excès, trop détachée de l’histoire, elle légifère souvent pour un homme de convention, indépendant de tout milieu social défini. Les progrès qu’ont accompli, au xixe siècle, les sciences politiques, sous l’influence de l’histoire et des philosophies inspirées de l’histoire, progrès vers lequel s’orientent, à la fin du siècle, toutes les sciences morales, la philosophie de l’éducation doit l’accomplir à son tour.
L’éducation est chose sociale : c’est-à-dire qu’elle met en contact l’enfant avec une société déterminée, et non avec la société in genere. Si cette proposition est vraie, elle ne commande pas seulement la réflexion spéculative sur l’éducation, elle doit faire sentir son influence sur l’activité éducative elle-même. En fait, cette influence est incontestable ; en droit, elle est souvent contestée.
Éducation et sociologie . Émile Durkheim. Texte établi par Paul Fauconnet, Librairie Félix Alca
Questions:
· Quel est la nature de l'éducation ?
· Quel est le rôle de l'éducation ?
· Quel est l'importance de l'éducation dans la vie de l'homme
· Quelle est la différence entre l'éducation et l'apprentissage ?
· Quel est l'objet de la sociologie de l'éducation ?
· Pourquoi l'éducation est la clé du développement ?
- المعلم: abdallah bouamrane
- المعلم: Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
- المعلم: Youcef HAMLAOUI
- المعلم: Leila Mahfoudi
- المعلم: Abd-Ennour SAMMAR
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA
- المعلم: Djalel Eddine GHERISSI
Rappeler et acquérir aux étudiants les connaissances fondamentales sur les enzymes et approfondir leurs connaissances en termes d’applications biotechnologiques de ces enzymes et de l’enzymologie dans les domaines : industriel, médicale, agroalimentaire et environnemental.
- Dr. SAOUDI Boudjema (MCB Biochimie UMCM): Boudjema SAOUDI
- المعلم: Manel BOULOUDENINE
- المعلم: Fahima Djefaflia
- المعلم: Youcef HAMLAOUI
- المعلم: Nedjem-Eddine BENCHOUIA
- المعلم: Med Tahar CHEFROUR
- المعلم: Abdelouahab MESSOUBER
- المعلم: Kamel MESSAOUDI
- المعلم: mounia AOUISSI
- المعلم: Radia MANAMANI
- المعلم: Radia MANAMANI
- المعلم: Chahinez BOUALLEG

International administrative law is a vital element in the international legal system. It defines the legal framework within which international organizations operate and ensures that their administrative activities are conducted fairly, transparently, and accountably. By establishing rules and procedures for decision-making, accountability mechanisms, and procedural safeguards, international administrative law enhances the effective performance of international organizations and protects the rights and interests of individuals and states.
- المعلم: Imad ICHOUI
- المعلم: Atef BENHAOUES
- المعلم: kais khoualdia
- المعلم: Nadia BENATI
- المعلم: Nouredine GASMALLAH
- المعلم: Atef BENHAOUES

Electronic marketing for services is a vital area that is gaining increasing importance in the era of information and communication technology. With the growing reliance on the internet as a primary means of communication and interaction, organizations need effective marketing strategies that allow them to reach a wider audience and enhance their digital presence.
This course aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the concepts and strategies of electronic marketing, focusing on how to promote services through digital channels. It covers various tools and techniques used in digital marketing, such as Search Engine Optimization (SEO), social media marketing, and email marketing, as well as data analysis and performance evaluation.
This course will help students develop their skills in designing and implementing innovative marketing strategies that align with changing market needs and achieve tangible results. Through case studies and analysis of current trends, participants will be able to understand the challenges and opportunities presented by electronic marketing for services.
This course we will explore the following areas:
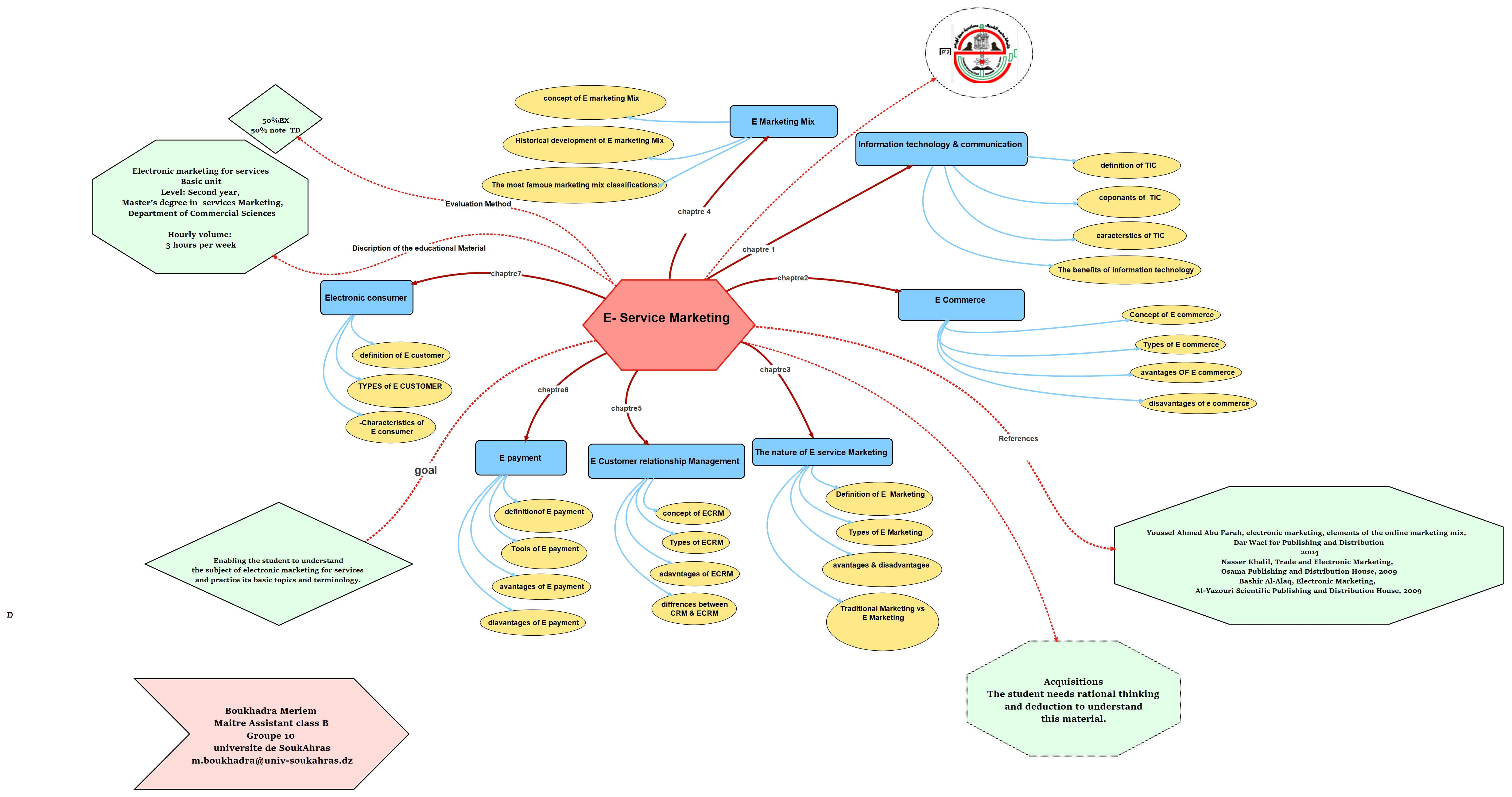
- المعلم: meriem boukhadhra
- المعلم: Meriem BOUKHADRA


- Public international law is defined as the body of legal rules and principles that govern the relations between states and other international entities, such as international organizations.
- It is distinct from private international law, which deals with conflicts of laws across different jurisdictions involving private individuals.
- المعلم: Asma GOUASMIA
- المعلم: Lynda YECHOUI
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE
- المعلم: Mohammed Saaidia
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI

Day by day, to Satisfy their energy needs, industrial societies pollute our environment. Around 90% of the world’s fossil fuel production is yearly extracted from the subsoil. In 1989, 3.5 billion tons of coal,3.1 billion tons of oil and 1.4 billion tons of gas were extracted. The transport of fuels accounts for around half of the maritime traffic. A significant proportion of the eight billion tons/year flow of fossil fuels is burned, and the combustion products are discharged untreated into the environment, mainly into the atmosphere. The challenge of producing the energy needed to satisfy world consumption without depleting resources and damaging the planet’s environment. However, it is necessary to focus on renewable energy solutions: wind power, solar energy power biomass and other renewable energy. nevertheless, the current share of this promising new form of energy in global products is around 15%.
- المعلم: Zohir BOUMOUS
- المعلم: Ilheim Derradji
Day by day, to Satisfy their energy needs, industrial societies pollute our environment. Around 90% of the world’s fossil fuel production is yearly extracted from the subsoil. In 1989, 3.5 billion tons of coal,3.1 billion tons of oil and 1.4 billion tons of gas were extracted. The transport of fuels accounts for around half of the maritime traffic. A significant proportion of the eight billion tons/year flow of fossil fuels is burned, and the combustion products are discharged untreated into the environment, mainly into the atmosphere. The challenge of producing the energy needed to satisfy world consumption without depleting resources and damaging the planet’s environment. However, it is necessary to focus on renewable energy solutions: wind power, solar energy power biomass and other renewable energy. nevertheless, the current share of this promising new form of energy in global products is around 15%.
- المعلم: Zohir BOUMOUS
- المعلم: Ilheim Derradji
This course is destinated to the students of the second year of the graduate studies of "Sciences and Technologies (ST)".
The course is devided in three chapters :
Chapter I : Basic laws and fundamental electrical analysis methods.
Chapter II : Two-port networks and filters
Chapter III: Electronic components and applications
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA
- المعلم: Mohammed Saaidia
Semestre : 3
Unité d’enseignement : UEM 2.1
Matière : Management des projets
VHS : 22h30 (Cours : 1h30)
Crédits : 2
Coefficient : 1
Objectifs de l’enseignement :
L’objectif de ces enseignements est d’Initier l’étudiant aux bases fondamentales et modernes du management des projets
Connaissances préalables recommandées
Le cours ne requiert pas de connaissances spécifiques préalables.
Contenu de la matière :
Chapitre 1 : Introduction au management des projets. (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 2 : Historique du management des projets. (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 3 : Management moderne des projets. Approche systémique. (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 4 : Les fonctions managériales. (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 5 : Définir le projet. Le WBS (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 6 : Estimation de la durée et des couts du projet. (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 7 : Planning et programmation dans les projets. (2 Semaine)
Chapitre 8 : Les ressources humaines. (2 Semaine)
Chapitre 9 : La motivation. (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 10 : La décision. (1 Semaine)
Chapitre 11 : Le leadership et leaders (1 Semaine)
Mode d’évaluation :
100% examen
- المعلم: Abdelkrim GUEBAIL
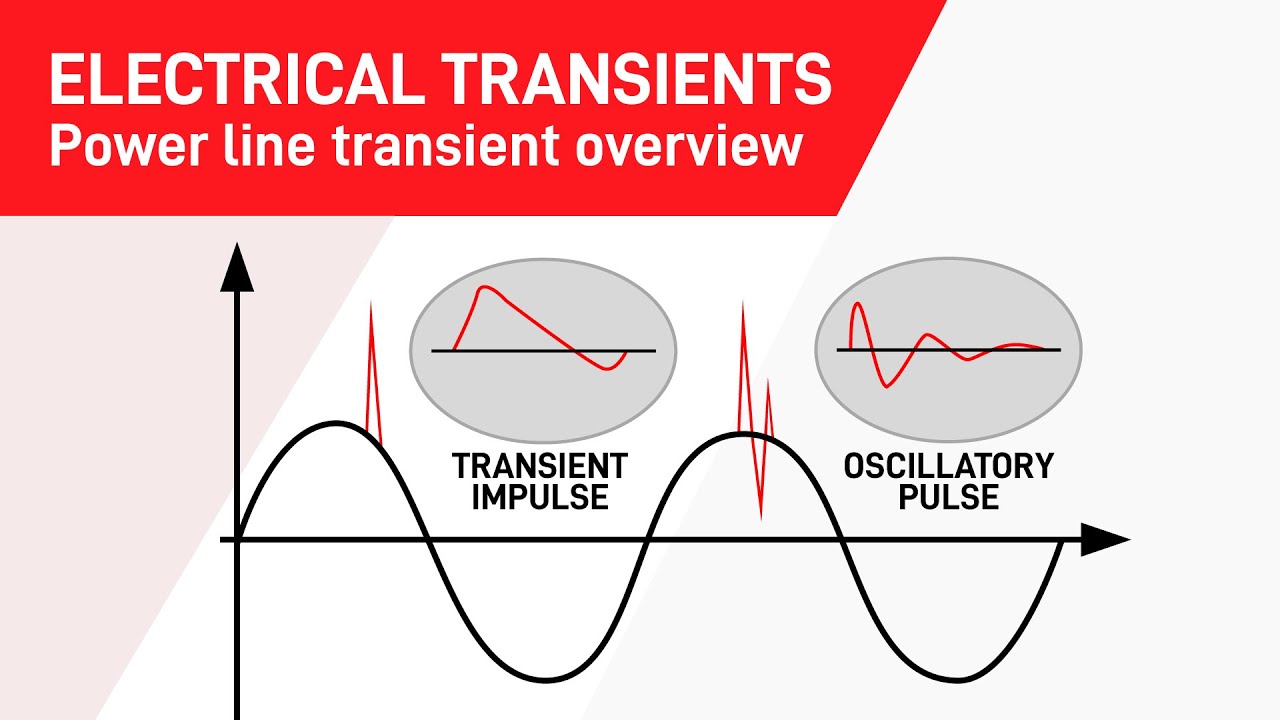
The transient regime in electric machines refers to the dynamic state during which the machine's operating conditions are changing rapidly, such as during startup, shutdown, or sudden changes in load. During these transient periods, the electrical and mechanical characteristics of the machine undergo significant variations, leading to transient phenomena such as voltage and current spikes, torque fluctuations, and mechanical stresses. Understanding and managing the transient regime is crucial for ensuring the reliable operation and longevity of electric machines. Techniques such as transient analysis, simulation, and control strategies are employed to predict and mitigate the effects of transients, optimizing the performance and efficiency of electric machines across various applications, from motors and generators to transformers and actuators. By addressing transient behavior, engineers can enhance the stability, reliability, and safety of electric machine systems, ultimately contributing to advancements in energy efficiency and industrial automation.
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
The course covers basic physical theory of semiconductors:
• Band structure, intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors - charge carrier concentrations and transport phenomena
• Non-equilibrium in semiconductors: excitation and recombination mechanisms, charge carrier injection • understanding of key parameters of semiconductor materials
• Properties and function of components such as pn junctions, metalsemiconductor junctions, transistors and solar cells.
The overall objective of the course is to provide in-depth knowledge of the fundamental physical principles needed to understand semiconductor devices and their function. The course connects to courses in solid state physics or equivalent.
- المعلم: Rebiha Marki
- المعلم: Yassine Sayad
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
The practical works aim to deepen students' understanding of fundamental physics concepts through hands-on experiments. In the Kundt tube experiment, students visualize standing waves and measure sound speed, enhancing their observational and analytical skills. The wave propagation on the water surface allows them to explore resonance phenomena, data collection, and analysis in a real-world context. Finally, the electrical oscillating circuits experiment provides insights into RLC circuits, resonance, and impedance, while fostering skills in circuit analysis and practical experimentation. Overall, these experiences cultivate critical thinking, collaboration, and scientific literacy, essential for future studies and careers in STEM fields.
- المعلم: dikra bouras

The practical works aim to deepen students' understanding of fundamental physics concepts through hands-on experiments. In the Kundt tube experiment, students visualize standing waves and measure sound speed, enhancing their observational and analytical skills. The wave propagation on the water surface allows them to explore resonance phenomena, data collection, and analysis in a real-world context. Finally, the electrical oscillating circuits experiment provides insights into RLC circuits, resonance, and impedance, while fostering skills in circuit analysis and practical experimentation. Overall, these experiences cultivate critical thinking, collaboration, and scientific literacy, essential for future studies and careers in STEM fields.
- المعلم: dikra bouras

The practical works aim to deepen students' understanding of fundamental physics concepts through hands-on experiments. In the Kundt tube experiment, students visualize standing waves and measure sound speed, enhancing their observational and analytical skills. The wave propagation on the water surface allows them to explore resonance phenomena, data collection, and analysis in a real-world context. Finally, the electrical oscillating circuits experiment provides insights into RLC circuits, resonance, and impedance, while fostering skills in circuit analysis and practical experimentation. Overall, these experiences cultivate critical thinking, collaboration, and scientific literacy, essential for future studies and careers in STEM fields.
- المعلم: dikra bouras
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA
- المعلم: chaouki Moumeni
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE

This course provides university students with a comprehensive understanding of the principles and practices of research in academic settings. It introduces the fundamental concepts of research design, data collection, analysis, and interpretation, emphasizing both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Students will learn to formulate research questions, develop hypotheses, select appropriate methodologies, and critically evaluate existing research literature. The course also covers ethical considerations, validity, reliability, and the proper documentation and presentation of research findings. By the end of the course, students will be able to design and conduct independent research projects, analyze data rigorously, and effectively communicate results in written and oral formats. This course is essential for students intending to pursue advanced studies, thesis projects, or careers requiring research competence.
- المعلم: SALAH SALAH Naima
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: chaouki Moumeni
Plant physiology, or phytobiology, is the science that describes how plants function in all aspects — anatomical, histological, cytological, and molecular — at every level (cell, tissue, organ, organism), and in relation to their environment (soil, water).
Plant physiology studies the mechanisms that govern the functioning and development of plants.There are two main areas:
Nutrition and Metabolism:The acquisition of elements essential for life (carbon- or nitrogen-based substances);The transformation of these elements and their integration into organic matter (biomass).
Growth and Development: Mechanisms involved in the transition of a seed from a dormant state to a reproductive state (developmental cycle).

- المعلم: Fatima Zahra Chemouri
- المعلم: Yassine Sayad
- المعلم: Rebiha Marki
- المعلم: Nor REBAH
- المعلم: souheila bouacherine
- المعلم: Yacine AIT AMAR
- المعلم: souheila bouacherine
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Hassen Kaddour
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE
-Matière : Recherche documentaire et conception de mémoire.
· Public cible : master 2 Electrotechnique industrielle
· Les objectifs généraux : Donner à l’étudiant les outils nécessaires afin de rechercher l’information utile pour mieux l’exploiter dans son projet de fin d’études. L’aider à franchir les différentes étapes menant à la rédaction d’un document scientifique. Lui signifier l'importance de la communication et lui apprendre à présenter de manière rigoureuse et pédagogique le travail effectué.
- المعلم: hesna aberkane
- المعلم: salaheddine farhi
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE

The Sampling Techniques course plays a key role in the training of Master’s students (2nd year), specialization in Aquatic Ecosystems. It aims to provide them with the theoretical and practical foundations necessary for the reliable collection and interpretation of ecological data, using both probabilistic (simple random, systematic, stratified, etc.) and non-probabilistic sampling methods. These approaches form a methodological foundation essential for biodiversity assessment, habitat management, and environmental impact studies.
The course teaches students how to design sampling plans adapted to the diversity of aquatic environments, while addressing constraints related to sampling frequency, size, and specificity. It also covers the selection of relevant descriptors, the choice of variables to be measured, and the definition of appropriate observation scales, along with the spatial and temporal planning of field sampling campaigns.
Special attention is given to sampling techniques specific to aquatic ecosystems, focusing on major faunal groups, particularly vertebrates and invertebrates. Students are trained to design and carry out studies that meet scientific standards of accuracy and rigor while integrating issues of sustainability and ecosystem conservation.
Thus, this course aims to train competent and autonomous specialists, capable of designing and implementing sampling programs adapted to research and management needs in aquatic environments. It also contributes to developing cross-cutting skills in scientific methodology, critical data analysis, and environmental decision-making, which are essential for future careers in applied ecology and the conservation of natural resources.
- المعلم: imene boucenna
- المعلم: sarra GUERFI
meet.google.com/tjr-huqt-ojp
هذا الرابط الأفواج الثلاثة
وكل فوج يدخل وقت حصته مرحبا هذا هو رابط ليوم الخميس ثالث حصة
- المعلم: Madiha ATIK
Objectives of the subject are to acquire the fundamental elements of algebra, namely linear forms, bilinear forms on a finite-dimensional vector space, reduction of quadratic forms.
- المعلم: Bachir BARROUK
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE
- المعلم: Nor REBAH


- المعلم: Billel Ali srihen
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
- المعلم: Salima Meziane
- المعلم: Salima Meziane

The General Electronics module is intended for second-year Physics Bachelor's students (L2-S4) in the SM - Material Sciences field, Physics
- المعلم: HOUDA AMRI
- المعلم: Nor REBAH
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE

- المعلم: Billel Ali srihen
- المعلم: Riad TOUFOUTI
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
- المعلم: Abdesselam Bouguerra
- المعلم: Nor REBAH
- المعلم: HOUDA AMRI
- المعلم: Nor REBAH
- المعلم: Bilel ZERGUINE
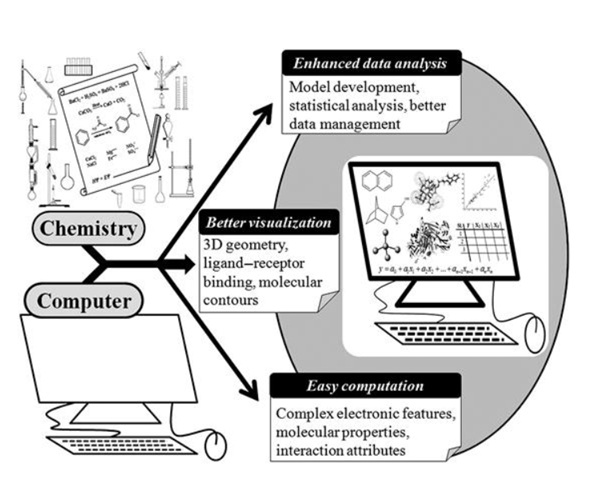
By the end of the lesson/module, students will be able to:
-
Explain the role and importance of computer tools in different areas of chemistry.
-
Recognize the basic features and functionalities of Unix/Linux operating systems commonly used in computational chemistry.
-
Apply statistical and graphical software for analyzing and visualizing chemical data.
-
Explore chemical databases indexed by molecular structure and retrieve relevant information effectively.
-
Describe and implement methodologies for scientific information retrieval in chemistry.
-
Demonstrate a basic understanding of molecular modeling concepts and tools for simulating chemical structures and reactions.
- المعلم: Sakina HAYAHEME
This
module is titled "Foundations of the Public Law". It has to do with individual,
group and peoples’ rights and freedoms. It aims at providing L3 students with
detailed understanding of these elements.
- المعلم: Fathi ZERARI

The course "Automatic English " is taught in the bachelor's degree program specializing in automation during the fifth semester . Its objectives are :
*Describing automatic equipment, how it works and its applications,
*expressing oneself on the subject of automation and
*In general,understanding a current affairs document .
In this course, we cover several topics. At the beginning, we review English grammar and conjugation. Then, with the aim of learning the terminology of automation, technical texts are covered, such as a text on programmable logic controllers, a text on electric cars, a text on robots, etc. Next, we learn techniques for presenting reports and summary memos. At the end, learners give presentations on the field of automation.
- المعلم: hesna aberkane
- المعلم: Ilheim Derradji

The electrical systems design course is intended for third-year electrical engineering students. Its main objective is to teach students how to calculate and dimension an electrical machine according to the requirements of a specific set of specifications.
In this course, we first illustrate the different parts of the electrical system .Then, based on certain assumptions and following certain calculation steps, we calculate the different main dimensions of the magnetic circuit, the electrical circuit, the types of insulation, the types of cooling,.. etc. The electrical systems are dimensioned as follows : single-phase transformers, direct current machines, asynchronous machines, synchronous machines, and finally special machines.
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Ilheim Derradji
- المعلم: Warda MOUMNI
- المعلم: Warda MOUMNI

The objective of this course is to acquire the basic theoretical knowledge of different electronic functions necessary to design and implement a transmission system. Functions as diverse as analog filters, amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation/demodulation, PLLs, etc. are covered.
- المعلم: Atef BENHAOUES
- المعلم: Lotfi MOUSSAOUI
- المعلم: Farid Berrezzek
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Saida HASSAINIA
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Saida HASSAINIA
- المعلم: hesna aberkane
- المعلم: Fatma KHAMMAR
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA
- المعلم: Zoubir ZAHZOUH
- المعلم: Khoutir BENTAHAR

Lab: Separation Techniques
The Laboratory Work: Separation Techniques teach students the key ways to separate, clean, and recognize the parts of a chemical mixture.
It includes classic methods like filtration, decantation, liquid-liquid extraction, and using a rotary evaporator to remove solvents, as well as modern techniques like column chromatography (CC) and thin-layer chromatography (TLC).
By the end of the course, students will be able to:
- understand the physical and chemical principles of each separation method;
- select the most appropriate technique depending on the type of mixture;
- and analyze chromatographic results to identify or assess product purity.
Learning Objectives
- Master classical and chromatographic separation methods.
- Relate molecular polarity to chromatographic behavior.
- Handle laboratory equipment (separatory funnel, rotavapor, chromatography column, etc.).
- المعلم: Mohamed ZABAT

Dedicated to 3rd year electronic students
- المعلم: Lotfi MOUSSAOUI
- المعلم: Mohammed Saaidia

Course Description:
This course provides an introduction to the various materials used in electrotechnical applications, focusing on their electrical, thermal, mechanical, and magnetic properties. Students will explore the fundamental materials essential for the design, production, and maintenance of electrical and electronic systems, including conductors, insulators, semiconductors, and magnetic materials. The course will also cover the selection criteria for these materials based on their performance and suitability in real-world applications such as power transmission, electronics, and energy storage systems.
Through practical examples, students will gain a solid understanding of how different materials are used in transformers, motors, capacitors, conductors, and electronic components, as well as the key factors that affect their choice in industrial and commercial settings.
Learning Objectives:
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
-
Identify and classify the key materials used in electrotechnical applications.
-
Understand the electrical, mechanical, thermal, and magnetic properties that determine material selection.
-
Explain the role of conductors, insulators, semiconductors, and magnetic materials in electrotechnical systems.
-
Analyze material behavior in real-world applications, such as electrical power transmission, electronic devices, and energy storage.
-
Make informed decisions about material selection based on performance, cost, and availability.
Key Topics:
-
Introduction to Electrotechnical Materials
-
Types of materials and their role in electrical engineering.
-
-
Conductors and Insulators
-
Materials for power transmission and insulation.
-
-
Semiconductors
-
Properties and applications in electronics.
-
-
-
Role of magnetic materials in transformers, motors, and inductive components.
-
-
-
Materials for capacitors and energy storage.
-
-
Material Properties and Performance
-
Electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical strength.
-
-
Emerging Materials
-
Advanced materials like graphene and composites in modern electrotechnical applications.
-
- المعلم: Khaddoudja GHADJATI
- المعلم: Samira BOUMOUS

The electric grid is a complex network that generates, transmits, and distributes electrical energy from power plants to consumers. It ensures that electricity is available everywhere, at any time, with stable voltage and frequency. Studying electric grid energy is very important because it helps engineers understand how to balance generation and demand, prevent power outages, and improve the efficiency of the system. The modern grid is becoming “smart,” using digital technology to monitor and control energy flow, integrate renewable sources like solar and wind, and reduce environmental impact. In summary, the electric grid is the heart of the energy system that powers our daily life and future development.
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER

- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
- المعلم: hesna aberkane

- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Hicham ZAIMEN
- المعلم: Atef BENHAOUES
- المعلم: Lotfi MOUSSAOUI
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Saida HASSAINIA
- المعلم: hesna aberkane
- المعلم: Fatma KHAMMAR
- المعلم: Fethi CHOUAF
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
- المعلم: Samira BOUMOUS
Biochimie Cellulaire et Fonctionnelle
Unité: Fondamentale
Crédit : 6
Coefficient 3 Niveau : Licence 3 Code UE : UEF3.1.1
INFORMATIONS GENERALES
INTRODUCTION
Ce document présente les objectifs, le contenu et les modalités d’évaluation du module Biochimie Cellulaire et Fonctionnelle.
Il est mis à la disposition des étudiants sur la plateforme pédagogique de la Faculté des Sciences de la Nature et de la Vie.
TEMPS CONSACRE
4heures 30minutes
CONTACT – RESPONSABLE DU COURS
Pr. Radia DRAIAIA
r.draiaia@univ-soukahras.dz
Description du cours
Préface
La biochimie cellulaire et fonctionnelle explore les mécanismes chimiques et moléculaires qui
assurent la vie de la cellule. Ce cours propose une vision intégrée des structures cellulaires, de leurs fonctions et de leurs interactions,
afin de comprendre comment leur coordination garantit le bon fonctionnement de l’organisme.
Il est organisé en six chapitres : Il débute par une présentation générale de la compartimentation cellulaire, puis aborde la structure et la
fonction des biomembranes ainsi que les mécanismes d’échanges et de reconnaissance. Les chapitres suivants traitent des relations
structure-fonction des organites, du rôle du cytosquelette, de la biosynthèse et de la dégradation des protéines. La glycosylation des
macromolécules et son importance biologique y sont également étudiées. Le module explore ensuite les mécanismes de transduction du signal, leur régulation et les cascades de signalisation. Enfin, il met en évidence les anomalies moléculaires responsables de diverses pathologies, notamment celles liées à la signalisation et au mauvais adressage protéique.
La visée générale du cours est de permettre à l’étudiant de comprendre l’organisation structurale et fonctionnelle de la cellule, d’expliquer les principaux mécanismes biochimiques qui régulent ses échanges et sa communication, et d’établir le lien entre altérations moléculaires et pathologies.
- المعلم: Radia DRAIAIA

The Methodology of Academic Research module introduces students to the principles, methods, and techniques necessary to conduct rigorous and systematic research. It covers the full research process, including identifying a research problem, formulating research questions and hypotheses, selecting participants, conducting literature reviews, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting findings. The module emphasizes both theoretical understanding and practical application, equipping students with the methodological tools, critical thinking skills, and academic rigor required to undertake independent research projects successfully.
- المعلم: asma TERRAB

Servo and regulated systems are closed-loop systems whose output precisely follows the input: the regulator wants the output to take on a precise value equal to the fixed input (the reference) regardless of the disturbance imposed, while the servo system (follower) wants the output to follow an input setpoint that varies over time and whose evolution is not always known in advance. All servo systems or control systems are represented by block diagrams, which include a comparison, power amplification, and measurement. This system is modeled by an differential equation that is often difficult to express and also difficult to solve. For this reason, the Laplace mathematical transform is crucial, as it allows us to move from a function f(t) where the variable is time “t” to a function F(p) where the variable is the complex Laplace operator “P” depending on the pulse ω.
After applying the Laplace transform to the system's differential equation, the dynamic system can be modeled by a transmittance, otherwise known as a transfer function, which is the ratio between the Laplace transform of its output and that of the input. This is valid when all initial conditions are zero. This function characterizes the dynamics of the system and depends only on its physical characteristics.
To calculate the temporal responses of the system, simply calculate the transmittance of the system, take the Laplace transform of the input signal, and multiply these two quantities. An inverse transform of the output signal gives the desired first-order or second-order time response of the system for different types of input (Dirac, step, ramp, and sinusoidal or harmonic input). The stability of servo systems (first-order and second-order) is analyzed using the Routh and Nyquist criteria. The accuracy and speed of the time responses (index, impulse) are assessed via the characteristics of the systems (first-order and second-order). Frequency analysis is also performed using the Bode diagram, which allows the stability and robustness of the closed loop to be evaluated.
- المعلم: ammar chakhrit
- المعلم: Ilheim Derradji

Servo and regulated systems are closed-loop systems whose output precisely follows the input: the regulator wants the output to take on a precise value equal to the fixed input (the setpoint or reference) regardless of the disturbance imposed, while the servo system (follower) wants the output to follow an input setpoint that varies over time and whose evolution is not always known in advance. All servo systems or control systems are represented by block diagrams, which include a comparison, power amplification, and measurement. The system's input time signal and output time signal are linked by a differential equation that is often difficult to express and also difficult to solve. For this reason, the Laplace mathematical transform is crucial, as it allows us to move from a function f(t) where the variable is time “t” to a function F(p) where the variable is the complex Laplace operator “P” depending on the pulse ω.
After applying the Laplace transform to the system's differential equation, the dynamic system can be modeled by a transmittance, otherwise known as a transfer function, which is the ratio between the Laplace transform of its output and that of the input. This is valid when all initial conditions are zero. This function characterizes the dynamics of the system and depends only on its physical characteristics.
To calculate the temporal responses of the system, simply calculate the transmittance of the system, take the Laplace transform of the input signal, and multiply these two quantities. An inverse transform of the output signal gives the desired first-order or second-order time response of the system for different types of input (Dirac, step, ramp, and sinusoidal or harmonic input). The stability of servo systems (first-order and second-order) is analyzed using the Routh and Nyquist criteria. The accuracy and speed of the time responses (index, impulse) are assessed via the characteristics of the systems (first-order and second-order). Frequency analysis is also performed using the Bode diagram, which allows the stability and robustness of the closed loop to be evaluated.
- المعلم: ammar chakhrit
- المعلم: Ilheim Derradji
- المعلم: Fahima ALI RACHEDI
- المعلم: Leila Mahfoudi
- المعلم: Rachida KHEMMAR
Découvrir les fonctions électroniques de base, comprendre leurs principes de fonctionnement, apprendre à les modéliser, être en mesure de les identifier dans un schéma électronique complexe.
- المعلم: Radhia BRAI
Maitriser le calcul des puissances monophasées et triphasées, connaitre les différents modes de couplage, déterminer les éléments des modèles équivalents, maîtriser le fonctionnement des différentes machines.


Child and Adolescent Psychopathology 1 is a core course designed for third-year students in School Psychology during the first semester.
By the end of the semester, students will have gained a solid foundation in child and adolescent psychopathology, understanding how disorders are classified, recognizing the unique features of early childhood, and becoming familiar with several psychological disorders commonly seen in children.
- المعلم: Ghada Bencheikh Lehocine

مقياس منهجية البحث وتحليل البيانات للسنة الثالثة ليسانس تخصص علم النفس المدرسي

- المعلم: amira saker
Donner aux étudiants la possibilité de réaliser des montages électroniques sur plaquette d'essai et de valider ensuite leur fonctionnement au moyen d'appareils de mesure.Comprendre et assimiler les lois fondamentales de l’électrotechnique, le fonctionnement des transformateurs et des moteurs.
- المعلم: mourad nahal
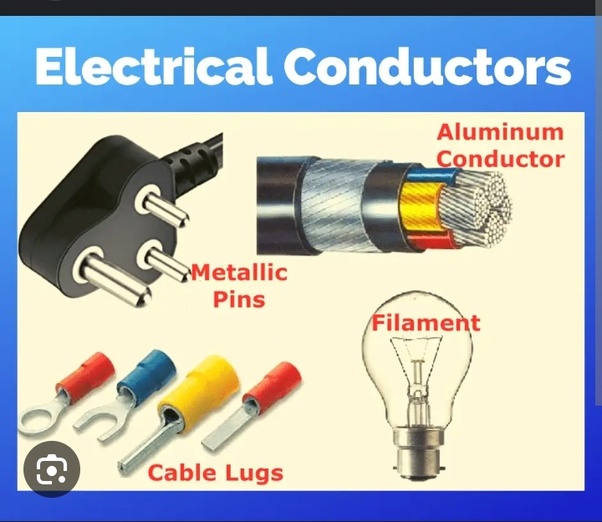
This lecture delves into :
- Electrical materials' fundamental principles and their role in various applications. It begins by exploring the nature of electrical materials, encompassing conductors, semiconductors, insulators, supraconduction, and magnetic materials elucidating their distinctive properties and behaviors under different conditions. The discussion extends to the significance of material selection in designing efficient electrical systems, highlighting considerations such as conductivity, resistivity, and dielectric strength. Furthermore, the lecture investigates the intriguing realm of high voltage phenomena, where electrical potentials exceed standard operating levels. It delves into the mechanisms underlying high voltage generation, transmission, and utilization, emphasizing the critical importance of safety measures and insulation techniques in mitigating associated risks. Through real-world examples and case studies, attendees gain insights into the applications, challenges, and advancements in high-voltage engineering, paving the way for a deeper understanding of this captivating field.
- Introduction to High Voltage:
High voltage, a realm where electrical potentials transcend conventional limits, represents a captivating yet inherently perilous domain within electrical engineering. Defined as voltages exceeding standard levels, typically beyond 1000 volts, high voltage phenomena command attention due to their profound implications across various sectors, including power generation, transmission, and industrial processes. At its core, high voltage engineering concerns the management and manipulation of electrical potentials beyond ordinary thresholds. This introductory segment illuminates the foundational concepts underpinning high voltage phenomena, encompassing voltage generation, transmission, and utilization. It underscores the significance of stringent safety protocols and robust insulation mechanisms to safeguard personnel, equipment, and infrastructure against the formidable hazards posed by elevated voltages.
- المعلم: Hicham ZAIMEN
Les nanosciences et nanotechnologies font de puis plus de vingt ans l’objet de nombreux travaux, au sein et à l’interface de disciplines scientifiques multiples, comme la physique, la chimie, la biologie, les sciences de l’ingénieur ou les sciences humaines et sociales. Les recherches sur les nanotechnologies suscitent des espoirs importants en raison des propriétés particulières de la matière à l’échelle nanométrique qui permettent d’envisager de nouvelles fonctions jusqu’ici inimaginables. Fabriquer, observer et manipuler des nano-objets, étudier et comprendre leurs propriétés et leurs interactions avec leur environnement, en particulier avec le vivant, les modéliser et les simuler, les intégrer dans des systèmes communicants, tels ont été et sont encore les grands défis scientifiques indispensables à relever pour développer des applications nombreuses et considérables, mais de façon maîtrisée et contrôlée. Les applications des nanotechnologies sont de plus en plus importantes dans la vie de chaque individu, pour l’industrie et le commerce, pour la santé et la société. Aujourd’hui, des travaux de recherche et de développement sont en pleine explosion sur les applications des nanotechnologies dans le domaine de l’énergie, de la chimie et des capteurs, des matériaux, de l’information et des communications, de la biologie et de la médecine, de l’environnement. Ce riche paysage ne doit pas occulter d’autres aspects, comprenant, en contrepoint des avantages, les risques nouveaux des nanotechnologies pour la santé, l’environnement, le respect de la vie privée, ou plus loin encore, les évolutions de l’espèce humaine. Les défis à relever sont donc immenses et la compétition entre grands pays apparaît de plus en plus acharnée.
- المعلم: Ouanassa GUELLATI
- المعلم: Naima HABIB
- المعلم: NAIMA HABIB
- المعلم: louardi YANDJAH
- المعلم: Alaoua BOUMZAOUET
- المعلم: Khayreddine CHOUAL
La protection des réseaux électriques est essentielle pour garantir la stabilité et la sécurité de l’approvisionnement en électricité. Elle permet d’éviter les pannes généralisées qui peuvent causer des interruptions de service, affectant ainsi les infrastructures critiques et l’économie. Les systèmes de protection détectent rapidement les défauts (surcharges, courts-circuits) et isolent les parties défectueuses pour limiter les dommages. Cela réduit les risques d’incendies et d’accidents électriques, protégeant ainsi les équipements et les personnes. Avec l’essor des énergies renouvelables et des réseaux intelligents, une protection efficace est nécessaire pour gérer la variabilité de la production. La cybersécurité est aussi un enjeu majeur pour prévenir les attaques informatiques visant les réseaux. Une bonne coordination entre producteurs, transporteurs et distributeurs est indispensable pour assurer la résilience du système. Enfin, l’innovation dans les technologies de protection contribue à une transition énergétique fiable et durable
- المعلم: Yacine DJEGHADER
- المعلم: Yacine AIT AMAR
- المعلم: Soumaya BATOUCHE
The goal of stereochemistry is to explain certain rules. For some specific points, such as the definition of configuration and conformation, for example, the terms, the stereochemistry of reacting molecules covers a very broad field, including, on the one hand, the influence of stereochemistry on the course of reactions, and on the other, the stereochemistry of the reaction products, taking into account the reaction mechanism. As well as other concepts such as stereospecificity in certain cases, the selectivity, reactivity, and geometry of compounds during reactions.
- المعلم: Djamel BOUCHOUK
- المعلم: Farid Berrezzek
- المعلم: Tahar BOUADJILA